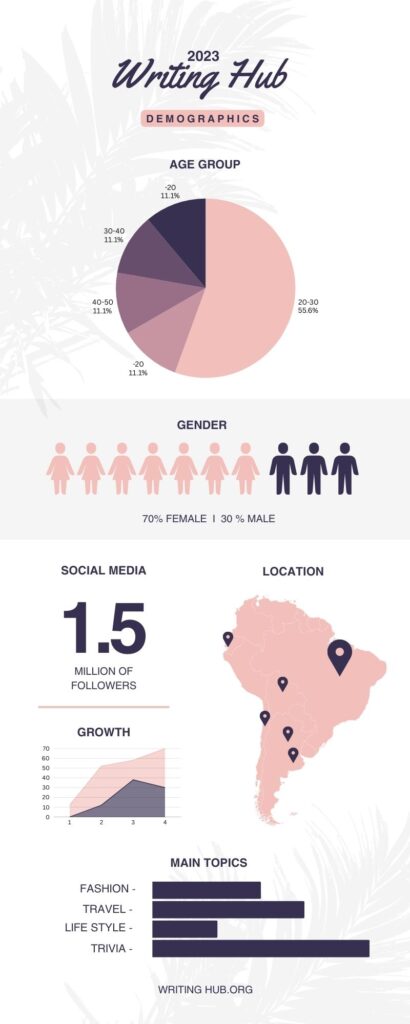
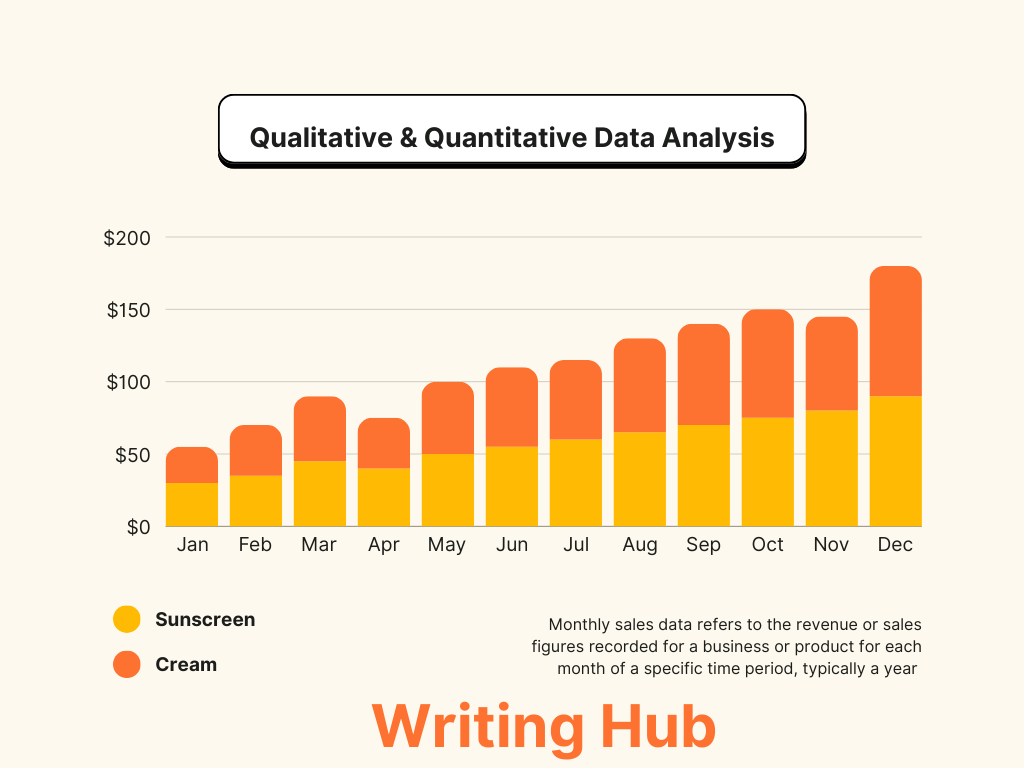
An In-Depth Guide for Thesis and Dissertation Writing
Data analysis is a critical component of thesis writing and dissertation writing, helping researchers make sense of their collected data and draw meaningful conclusions. Whether you are exploring human behavior, economic trends, or environmental factors, using the right data analysis methods is essential to ensuring that your research findings are robust and credible. This article explores the key differences between qualitative and quantitative data analysis, discusses their applications in research, and highlights best practices for choosing and implementing these techniques in thesis and dissertation projects.
Visit Writing Hub for guidance on implementing data analysis in your academic writing, ensuring a professional and credible approach.
Understanding Data Analysis: Qualitative vs. Quantitative
Data analysis involves the systematic examination of data to discover patterns, answer research questions, and support or refute hypotheses. Researchers can approach this process in two primary ways: qualitative data analysis and quantitative data analysis. Both methods are crucial in the field of academic research, and each offers unique benefits depending on the nature of the research.
Qualitative data analysis is typically used to interpret non-numeric data and understand complex, subjective phenomena. It’s ideal for research that seeks to explore perceptions, motivations, and experiences. On the other hand, quantitative data analysis is a more statistical approach that focuses on numeric data, making it suitable for studies that require objective measurements and quantitative comparisons.
Qualitative Data Analysis: Exploring the Depths of Subjective Data
Qualitative data analysis is an invaluable tool in fields such as psychology, sociology, anthropology, and other disciplines where understanding human behavior and experiences is key. This analysis type delves deeply into non-numeric data such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and open-ended survey responses.
Key Techniques in Qualitative Data Analysis
- Thematic Analysis: A popular method for qualitative research, thematic analysis involves identifying recurring themes or patterns within the data. This technique is commonly used in dissertation writing for humanities and social sciences, allowing researchers to draw insights based on participants’ experiences.
- Content Analysis: This method systematically categorizes and quantifies textual information, allowing researchers to uncover patterns and relationships in the content. Content analysis is often used in fields like media studies and linguistics.
- Narrative Analysis: Used when data is collected in story form, such as in narrative interviews, this method helps researchers understand the experiences and meanings that individuals attach to events.
- Discourse Analysis: This approach studies language and communication, examining how language reflects social, cultural, or political contexts.
When conducting qualitative data analysis for a thesis or dissertation, it is essential to document the steps you take for each analysis stage. Transparency in these methods strengthens the credibility of your findings and demonstrates your analytical rigor. At Writing Hub, we offer guidance on incorporating qualitative analysis in your academic writing, ensuring your approach is well-documented and credible.
Quantitative Data Analysis: The Power of Numbers in Research
In contrast, quantitative data analysis involves analyzing numeric data to test hypotheses, identify correlations, and make predictions. This type of analysis is particularly popular in fields like economics, psychology, biology, and the physical sciences.
Key Techniques in Quantitative Data Analysis
- Descriptive Statistics: Descriptive statistics summarize basic features of the data through measures such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. This method is typically the first step in thesis writing, providing an overview of the dataset.
- Inferential Statistics: Going beyond description, inferential statistics allow researchers to make generalizations about a population based on sample data. Common techniques include regression analysis, t-tests, and ANOVA (Analysis of Variance).
- Correlation and Causation Analysis: By calculating the relationship between variables, researchers can assess how one variable might influence another. This approach is crucial in dissertation writing that aims to establish causation or correlation.
- Factor Analysis: This advanced method identifies underlying variables, or factors, that explain the patterns in a dataset, especially useful in psychology and social sciences.
- Data Visualization: Although not strictly a statistical method, data visualization plays an essential role in quantitative data analysis by making patterns and insights more accessible. Graphs, charts, and tables enable readers to understand complex datasets quickly.
When using quantitative data analysis in a thesis or dissertation, it’s crucial to select methods that align with your research questions and hypothesis. For detailed guidance, Writing Hub offers tailored support in choosing the right statistical tools for your research objectives.
Choosing Between Qualitative and Quantitative Data Analysis
Selecting the right data analysis method largely depends on your research question, data type, and overall study design. In some cases, a mixed-methods approach—combining qualitative and quantitative methods—can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem.
Considerations for Choosing a Data Analysis Method
- Research Objective: If your goal is to explore in-depth motivations, opinions, or experiences, qualitative analysis is likely more suitable. However, if you are testing a hypothesis or measuring specific variables, quantitative analysis is generally preferred.
- Data Type: Non-numeric data, like interview transcripts, is better suited for qualitative analysis, while numeric data benefits from quantitative techniques.
- Study Scope: Quantitative analysis often requires larger sample sizes for statistical significance, whereas qualitative analysis can be meaningful with a smaller sample size.
- Disciplinary Standards: Different academic disciplines have their own conventions for research. For example, dissertation writing in the social sciences may require a qualitative approach, while thesis writing in the natural sciences might lean toward quantitative methods.
Whether you choose a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods approach, aligning your method with your research objectives and question is essential. At Writing Hub, we offer consulting services to help you select the appropriate analysis type for your thesis or dissertation, ensuring your research design is effective and suitable for your field.
Integrating Qualitative and Quantitative Data Analysis in Thesis and Dissertation Writing
For many students, a mixed-methods approach can provide a more nuanced perspective. By integrating both qualitative and quantitative data analysis, researchers can achieve a more holistic view of the research problem, balancing the depth of qualitative insights with the rigor of quantitative measurements. Here’s how you can integrate these approaches in thesis or dissertation projects:
- Sequential Explanatory Approach: In this approach, quantitative data is collected and analyzed first, followed by qualitative data collection. This sequence allows qualitative insights to explain or elaborate on quantitative findings.
- Sequential Exploratory Approach: Here, qualitative data is collected first to explore phenomena, followed by quantitative data to measure the extent of the phenomena observed. This approach is useful in hypothesis generation.
- Concurrent Triangulation: Both data types are collected simultaneously and analyzed together. This approach provides a balanced perspective, allowing for comparison and cross-validation of findings.
Using mixed methods adds depth to thesis and dissertation writing but requires careful planning to ensure both methods are integrated effectively. At Writing Hub, we specialize in helping students implement mixed-methods approaches, offering guidance to ensure each component aligns with their research goals.
Common Pitfalls in Data Analysis and How to Avoid Them
Both qualitative and quantitative data analysis require careful attention to detail. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for:
- Lack of Clear Research Questions: Without well-defined research questions, data analysis can become unfocused. Make sure each analysis method ties back to specific research objectives.
- Inadequate Documentation of the Process: Document each step in your analysis process, especially for qualitative research. This transparency strengthens the credibility of your study.
- Misinterpretation of Data: Be cautious when interpreting results, especially with quantitative data. Statistical findings need careful context to avoid overgeneralizations.
- Neglecting Ethical Considerations: Data analysis should respect ethical guidelines, including privacy and informed consent, particularly with qualitative data.
- Over-Reliance on Software: While tools like SPSS, NVivo, and Excel are invaluable, software alone cannot replace critical thinking and interpretation.
If you need assistance with navigating these challenges, Writing Hub provides support for both novice and experienced researchers, offering advice on avoiding common pitfalls and enhancing the quality of your analysis.
Final Thoughts: Enhancing Your Thesis or Dissertation with Effective Data Analysis
Effective data analysis is the foundation of strong research and plays a vital role in thesis writing and dissertation writing. Whether you’re working with qualitative or quantitative data—or a combination of both—choosing the right analysis methods ensures that your findings are reliable and relevant.
For personalized support in your academic journey, visit Writing Hub, where we offer expert guidance on every aspect of data analysis, thesis development, and dissertation completion. Our services are tailored to help you achieve clarity, consistency, and credibility in your research, ensuring your findings truly stand out.
With the right support, your research can be more than just a requirement—it can be a contribution that adds valuable insights to your field.